Предмет: Алгебра,
автор: artemaby
Помогите решить систему под : а,б,в
Приложения:

Ответы
Автор ответа:
0
Ответ:
напиши, пожалуйста, что написано под буквой "в", я не поняла значения
Приложения:
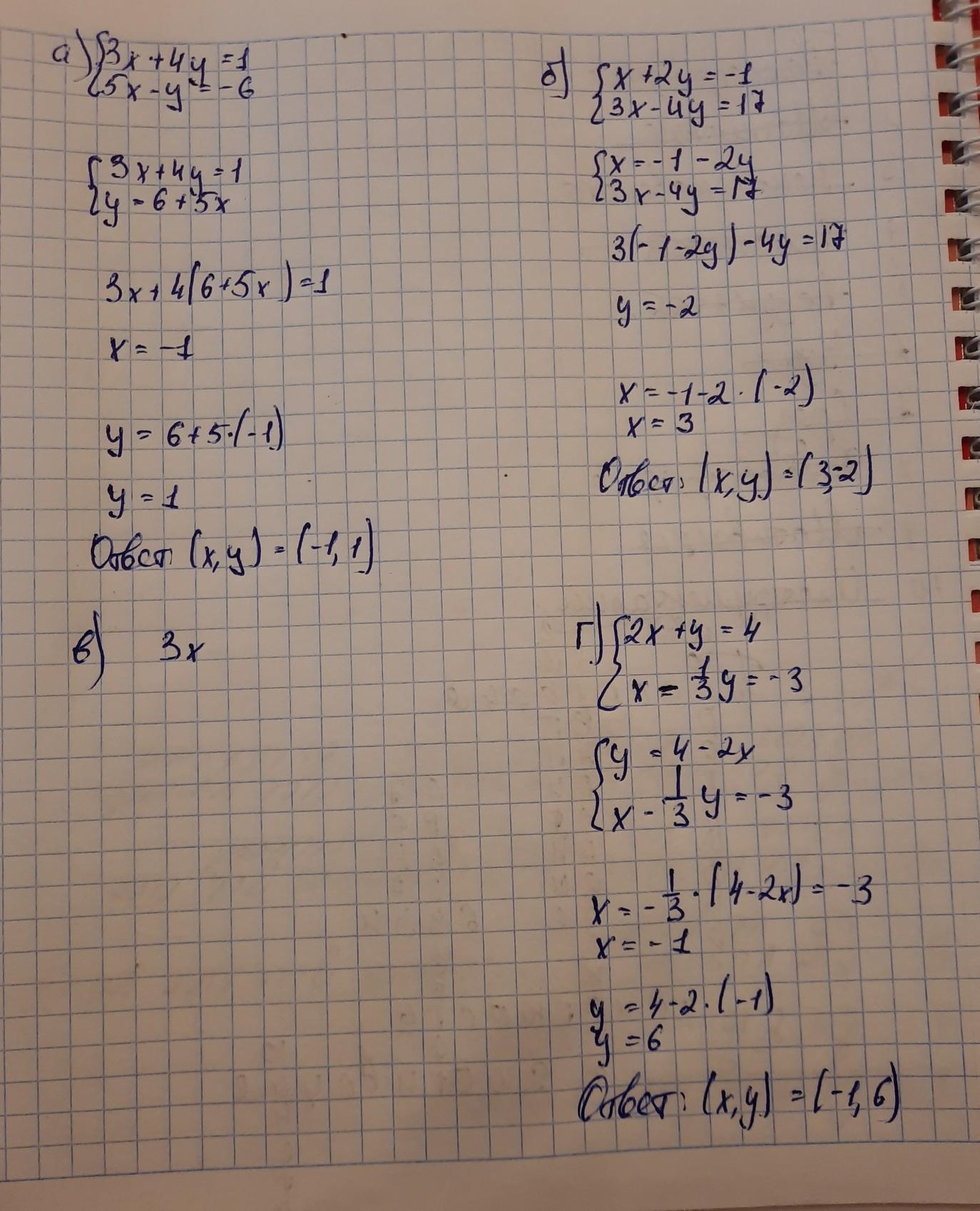
Похожие вопросы
Предмет: Английский язык,
автор: Ароян
Предмет: Английский язык,
автор: Школьница2007
Предмет: Английский язык,
автор: murkKotenka
Предмет: Английский язык,
автор: Likevif
Предмет: Биология,
автор: meleksalaxova