Предмет: Физика,
автор: ssliwwk
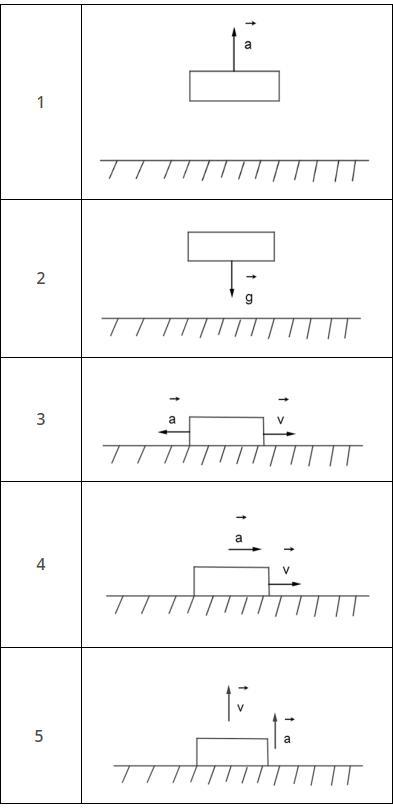
Для описанной ниже ситуации отметь рисунок, на котором указано направление ускорения, с которым движется рассматриваемое тело:
«ракета стартует с космодрома».
Выбери соответствующий номер рисунка
Приложения:
Ответы
Автор ответа:
0
Ответ:
5 рисунок
Скорость и ускорение сонаправлены вверх
Объяснение:
Похожие вопросы
Предмет: Русский язык,
автор: liliaranetcaia
Предмет: Русский язык,
автор: Шлольник
Предмет: Українська мова,
автор: MarySn12
Предмет: Информатика,
автор: vityazev95
Предмет: Физика,
автор: hdjd99