Предмет: Алгебра,
автор: girlinred93
решите уравнения методом замены новой переменной
Приложения:
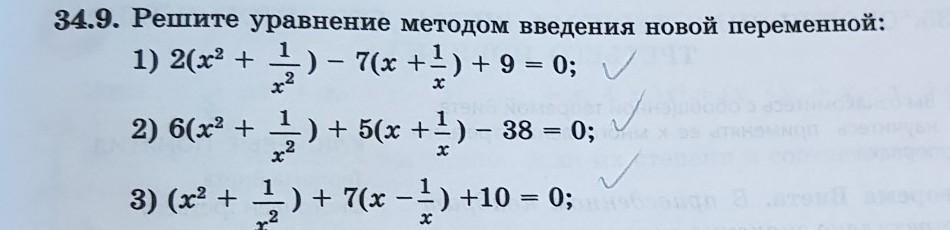
Ответы
Автор ответа:
1
Похожие вопросы
Предмет: Химия,
автор: Raccоon
Предмет: Алгебра,
автор: ElyaHar02
Предмет: Математика,
автор: galyaemelyanov
Предмет: История,
автор: Julia14151